CEMENT
A cement is a binder, a substance that sets and hardens and can bind other materials together. The word "cement" traces to the Romans, who used the term opus caementicium to describe masonry resembling modern concrete that was made from crushed rock with burnt lime as binder
IMPORTANCE OF CEMENT
Concrete is the most used material in the world because of its
cheap price and large quantity. It is needless to say concrete is made
of cement. However, cement is also a criticized material by the public,
for its intensive CO2 emission from production process. The production of cement accounts for about 5-8% of the non-natural CO2 worldwide.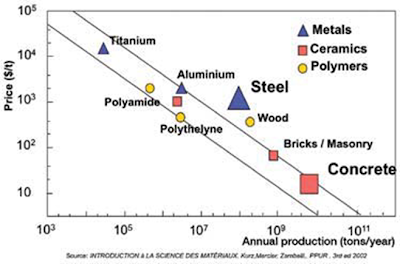


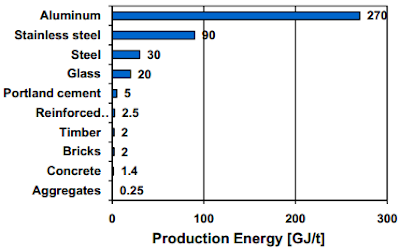
People may ask, can we find an alternative construction material instead of cement? such as wood, steel. The annual usage of wood is much above the replanting level, and it is not possible to get wood in some places such as Africa and China. As for steel, it is costly and again the production of steel also gives CO2 emission. Furthermore, the production of cement is not that energy intensive compared with other materials.
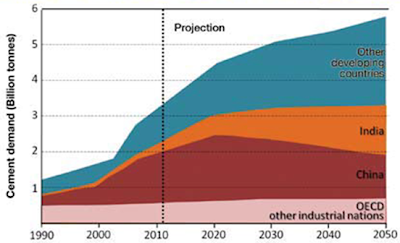
Actually, it is not possible to find an alternative construction material. 98% of the earth’s crust is made of eight elements: O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K, Mg, which are the main elements of cement as well. From the long term run, the world will still need a large amount of cement. The demand of cement mainly comes from developing countries, such as India and China because of the urbanization and its population growth.


Since we have to use cement in the future, how can we do to reduce the CO2 emission and what is the future of cement? Efforts have been doing ever since decades ago in the cement industry and research community.
On the one hand, cement plants nowadays burn (hazardous) waste, say, car tyres, as fuel to make cement. The wood floating on the water of Three Gorges Dam is even collected to make fuel for cement plants. On the other hand, the production process of cement has always been optimizing. Some cement plants can even reach 80% efficiency, which is a great achievement even from a theoretical standpoint.


Researchers of cement try to use less cement clinkers. One viable method is Supplementary Cementitious Materials (SCMs). SCMs are commonly industry by-products or raw materials, such as Slag, limestone, Fly ash, silica fume, natural pozzolan. Whether binary blended or even ternary blended, SCMs can replace part of cement without sacrificing equivalent engineering properties.

Considering the limited quantity and access of SCMs, SCMs are not a permanent sustainable way from a long term run. Some researchers are trying to utilize the unlimited amount of calcined clay, for the kaolinite content of clay has similar cementitious property. Work done replacing 30% of cement by calcined clay in Cuba shows the potential future of clay if well used.

Generally speaking, cement is a significantly important construction material, and it is not necessary to worry that much as for the CO2 emission in the future.
IN ALL THESE RESPECTS TESTING OF CEMENT HAS TO BE DONE. STANDARD SHOULD BE ADOPTABLE. SO PART OF TESTING OF VIDEOS GIVEN BELOW

